Explore Your Data with Tableau Agent
As of 14 October 2025, Data Cloud has been rebranded to Data 360. During this transition, you may see references to Data Cloud in our application and documentation. While the name is new, the functionality and content remains unchanged.
Tableau Agent is a generative AI feature that helps you explore your data, create visualisations and uncover insights with the help of a conversational assistant. Connect to a workbook or data source and use natural language to perform visual analysis. Use Tableau Agent and the Tableau UI together to get to insights faster. With Tableau Agent, staring at a blank canvas becomes a thing of the past.
In the Tableau authoring experience, you can open the Tableau Agent conversation pane in a worksheet. Tableau Agent can help with tasks like:
- Jump-start your analysis: Tableau Agent can suggest analytical questions based on your data
- Build a viz: "How many action films did each director make?"
- Choose the best chart type for an analysis: "Show me the distribution of student's marks"
- Perform time series analysis: "What month had the largest growth in the number of donors compared to the previous month?"
- Create calculated fields: "Create a field that calculates the difference between case open and closed dates and round up to weeks"
- Explain calculations: "Explain the ‘Days to Ship Actual’ calculation"
- Filter and sort data: "Only look at Saltwater and show me the fish with the smallest tank options"
Tableau Agent creates visualisations based on your data, just like Show Me in Tableau. Chart types that Tableau Agent can currently support include:
- Text
- Heatmap
- Bar
- Stacked bar
- Line
- Dual line
- Area
- Gantt
- Box plot
- Scatter plot
- Histogram
- Symbol map
- Filled map
- Tree map
- Pie
- Bullet
- Bubble
For more information about Tableau chart types, see Choose the Right Chart Type for Your Data(Link opens in a new window).
Note: To use this feature, you must sign in to a Tableau Cloud site that has Tableau+, and AI in Tableau must be turned on in your site settings. If you don't have Tableau+, but want to try Tableau Agent features, you can sign up for a Tableau Cloud free trial, which now includes Tableau Agent features. To start your trial, fill in this form or contact your Account Executive. For more information about the free trial or to configure AI in Tableau, see Turn on AI in Tableau for Your Site(Link opens in a new window).
Starting in version 2025.3, you can also use Tableau Agent if you are signed in to a Tableau Server site with AI in Tableau turned on. For more information, see Turn on AI in Your Tableau Server Site(Link opens in a new window).
Tableau Agent and Trust
Tableau Agent in Tableau Cloud is built on top of the Einstein Trust Layer(Link opens in a new window) and inherits all of its security, governance and Trust capabilities. As you interact with Tableau Agent, neither your data nor your conversations that are sent to the Large Language Model (LLM) are saved to the LLM, and no customer data is ever used to train the model.
Tableau Agent only works with the data sources your workbook is connected to. It isn’t aware of any other Tableau data sources, so it can’t suggest relevant content, answer data lineage questions or answer general-knowledge questions. User-defined policies for row- and column-level security are respected. The data a user has access to while using Tableau Agent conforms to any row or column-level security policies that you have in place.
When you first open Tableau Agent, it indexes your data to understand the context. This helps Tableau Agent return relevant results based on your questions and your data source. The information it indexes includes field metadata (field captions, field descriptions from comments in Tableau Desktop or from Tableau Catalog, data roles and data types) and samples of up to 1,000 unique field values if the data type is string (text).
Tableau Agent uses the field caption or alias, not the original field name. For example, if you rename ‘Host’ to ‘Owner’, Tableau Agent will recognise ‘Owner’ but might not recognise ‘Host’. Similarly, if you create an alias(Link opens in a new window) like ‘Breakout’ for ‘SessionType1’, it will recognise ‘Breakout’ but not ‘SessionType’. Tableau Agent can index field descriptions included as comments. For details on adding comments, see Add default comments for specific fields(Link opens in a new window).
The Einstein Trust Layer can be used to mask Personally Identifying Information (PII) before it is sent to the LLM using pattern-based data masking. Using machine learning and pattern matching techniques, PII in prompts are replaced with generic tokens and then unmasked with original values in the response. For more information about how to configure data masking, see Select What Data to Mask(Link opens in a new window) in the Salesforce help. For an additional layer of protection, the Einstein Trust Layer guarantees that after the prompt and response are processed by the LLM, the LLM forgets both the prompt and the response.
If you’re using Tableau Agent in Tableau Server (version 2025.3 and later), it doesn’t use the Einstein Trust Layer. Instead, you connect directly to your Large Language Model provider. For more information, see AI in Tableau and Trust(Link opens in a new window).
Tableau Agent billing considerations
Note: Starting in October 2025, AI in Tableau no longer consumes Einstein Request credits for AI usage. Other services, such as Data Cloud services, can still consume other types of credits. For more information, see Einstein Request & Flex Credit Rate Card Updates FAQ(Link opens in a new window).
When you use generative AI features in Tableau in Tableau Cloud, it may consume Data Cloud credits if you’re using the Einstein data collection and Storage (also known as Audit Trail) feature as part of your AI in Tableau setup. For more information, see AI in Tableau Usage(Link opens in a new window).
You can view your credit consumption in your Salesforce org using pre-built dashboards and Digital Wallet, or connect to your Data Cloud data from Tableau and build visualisations using the data from Digital Wallet tables. For more information, see View Credit Consumption(Link opens in a new window).
Get started with Tableau Agent
Note: Tableau Agent is not supported if you are using a Salesforce Government Cloud Org.
Tableau Agent is available through a conversation pane in the web authoring environment when AI in Tableau is turned on for your site. In Tableau Cloud, you can choose to turn it on for a single group of users or for all users on your site. For more information, see Configure AI in Tableau(Link opens in a new window).
Use Tableau Agent in:
Tableau Cloud (requires Tableau+)
Tableau Server (version 2025.3 and later)
Tableau Desktop (version 2025.1 and later) when signed in to a Tableau Cloud or Tableau Server site with AI in Tableau turned on for web authoring
Tableau Agent is only available for worksheets, so you won’t see this option in dashboards or stories.
In Tableau Cloud, you also must have the site role of Creator or Explorer to use this feature.
Starting in version 2025.1, Tableau Agent supports English (en_US) and a subset of other languages. If your Cloud site, Server site or Tableau Desktop application is set to a language that isn’t supported, Tableau Agent responses will be in English (en_US). For more information about supported languages, see AI in Tableau-supported languages and locales(Link opens in a new window).
Start by creating a new workbook or opening an existing one. For new workbooks, you start by connecting to your data. For faster results, we recommend using Tableau Agent with extracts. However, you can also use Tableau Agent with live database connections and uploaded files with the following file types:
.hyper
.csv
.txt
.xlsx
Tableau Agent doesn't support cubes. Also, if you're using data blending, Tableau Agent can only be used with the primary data source.
Launch Tableau Agent
To open the Tableau Agent conversation pane, do the following:
Select the Tableau Agent icon in the toolbar next to Show Me.
When the pane opens, select Got It to acknowledge the disclaimer and get started.
Build and change a viz
Tableau Agent isn't an open-ended chatbot. It can only work within your data set and perform a specific set of actions around analysis and viz creation. To understand your data, Tableau Agent starts by indexing the data set you’re connected to. If you’re connected to more than one data set, it will work with the selected data set shown in the Data pane. Tableau Agent only works with the primary data source in a data blend.
Note: If you switch to a different data source while Tableau Agent is processing your request, this can cause an error. Wait until Tableau Agent responds before changing data sources; then make a new request using that data source.
Indexing scans the field names and data types (such as dates, text or number fields), and samples 1,000 unique field values to get a sense of what kind of data is in that field. Re-indexing occurs periodically when a change is made, such as renaming a field or creating a new calculated field.
After indexing is complete, Tableau Agent provides some suggested questions you could ask about your data to help you get started, or type your own questions into the text box using natural language to describe what you want.
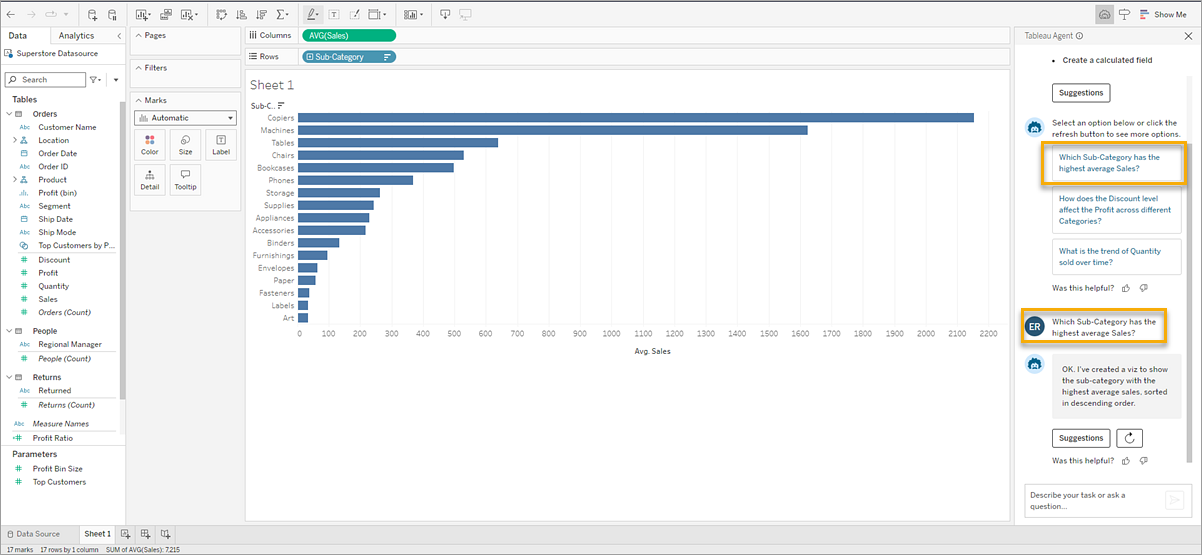
After Tableau Agent creates the viz, you can interact and modify it, just like if an analyst built and shared a viz with you. Ask more questions with Tableau Agent to iterate and explore your data further, use Suggestions to get more ideas about questions you can ask, or take the reins and continue your analysis on your own directly in the Tableau interface.
If the viz that Tableau Agent created isn't what you're expecting, you can either provide additional information by typing what you want in the text box, or try selecting the Retry with Tableau Agent  and Tableau Agent will query the LLM again and provide a new response to your request.
and Tableau Agent will query the LLM again and provide a new response to your request.
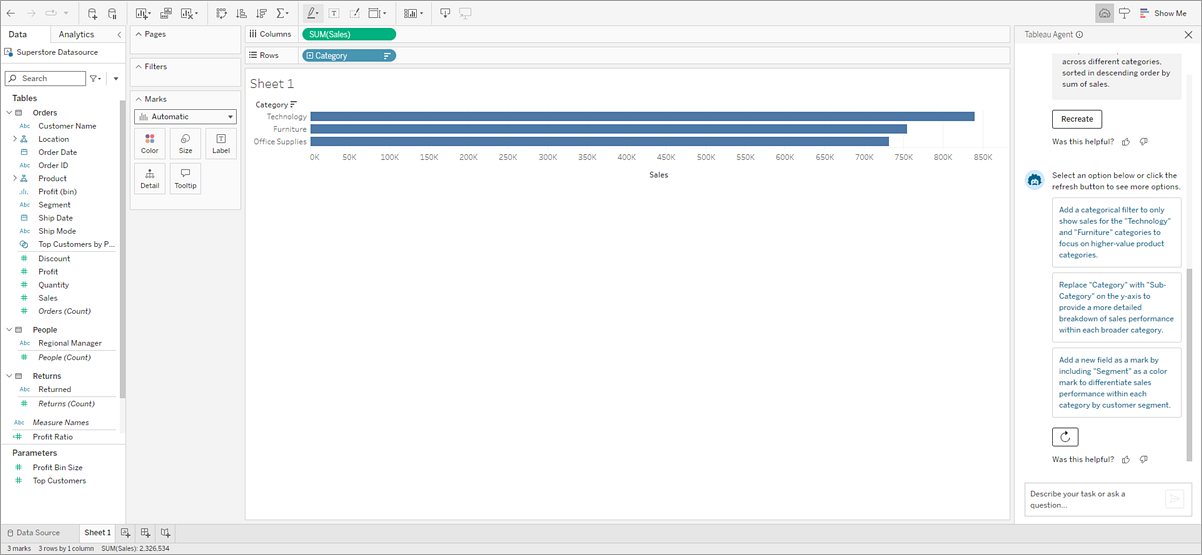
Use suggestions to jump-start your analysis
Whether you're facing a blank canvas or are deeper into your analysis, Tableau Agent can help by suggesting questions you can ask to dig deeper into your data. Before you begin, select the Suggestions button and Tableau Agent will create three questions you might ask based on your data source. To see more questions, select Retry with Tableau Agent  .
.
Select a question, and Tableau Agent creates the corresponding viz for you.
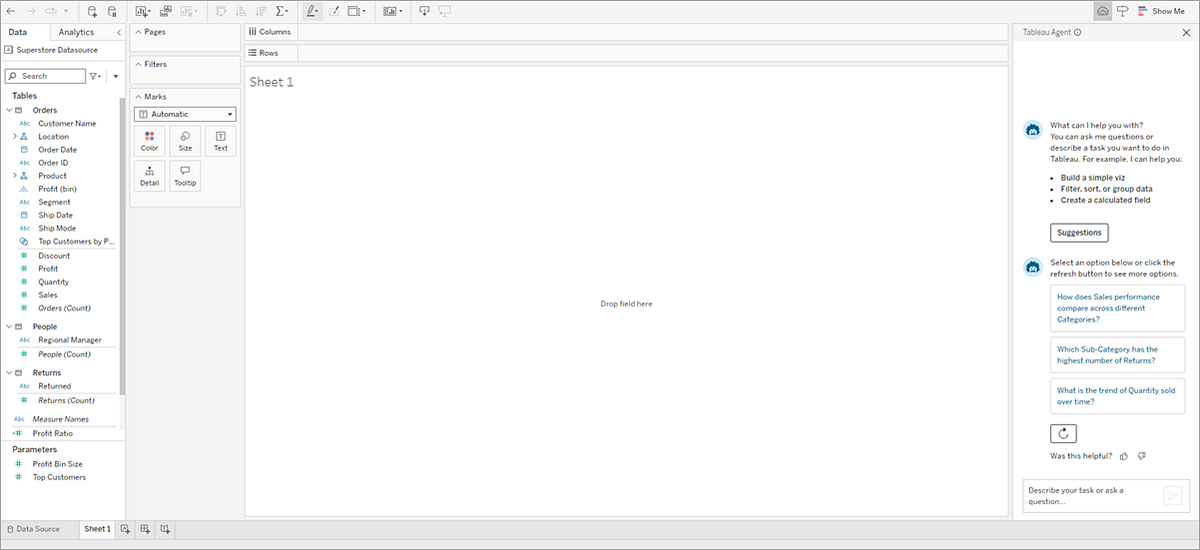
Use suggestions to dive deeper into your analysis as you interact with vizzes Tableau Agent has created.
Also, starting in version 2025.1, when you use Tableau Agent to create or modify a calculation and accept the calculation, Tableau Agent offers suggestions about how you might use the calculation in your analysis.
At the bottom of the confirmation response from Tableau Agent, select the Suggestions button and Tableau Agent will suggest some actions you might take to discover more insights about your data. When you do this, the Suggestions button is converted to a Recreate button so that you can go back and recreate the previous viz if needed.
Simply select an option to apply the suggested action to your viz. If you don't like those suggestions, just select Retry with Tableau Agent  to see more options.
to see more options.
Create calculations
Building calculations in Tableau can sometimes be tricky. If you're new to Tableau, you might not know the right syntax to use or how to properly format your calculation. Tableau Agent can do the heavy lifting for you, keeping you in the flow of your analysis.
Simply ask Tableau Agent to help you create a calculation using natural language to describe what you want to do. Tableau Agent does the following:
Opens the Calculation Editor
Adds the suggested syntax
Names the calculation
Provides an explanation of the calculation in the Tableau Agent pane to help you evaluate it for accuracy and build proficiency
Review the calculation, edit it if needed and accept it. Tableau Agent adds the new calculated field to the Data pane, and it’s ready to use in your analysis.
There are two ways to ask for help with calculations:
In the conversation pane: Ask Tableau Agent to create calculations for you as part of the flow of your conversation. Just describe your calculation using natural language, and Tableau Agent does the rest.
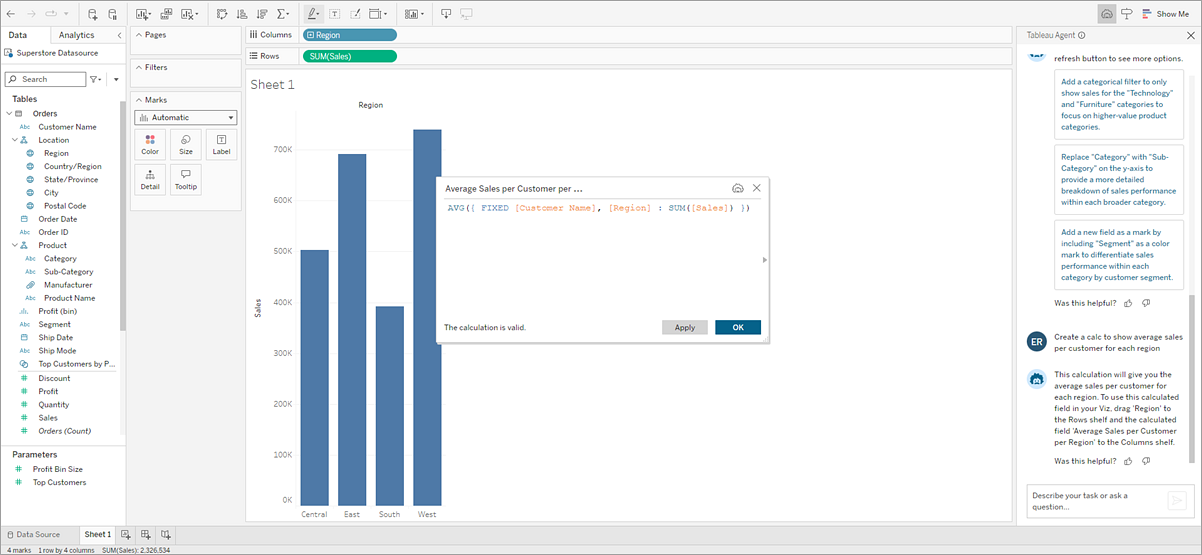
In the Calculation Editor: Open the Calculation Editor and select the Tableau Agent
 icon. This opens the conversation pane if it isn’t already open. If the conversation pane is open, just type your calculation description in the text box, and Tableau Agent adds the suggested syntax right into the open Calculation Editor.
icon. This opens the conversation pane if it isn’t already open. If the conversation pane is open, just type your calculation description in the text box, and Tableau Agent adds the suggested syntax right into the open Calculation Editor.
Tips for creating calculations
To get the best results when asking Tableau Agent to help you create a calculation, be specific. When your goal is to have Tableau Agent write a calculation for you, use that specific language. For example, “Create a calc…”, “Write a calc…”, “Create a calculated field…” or simply just “Calculate…”
It's also important to avoid being too generic. For example, instead of saying “Identify my most profitable products”, try “Calculate the profit ratio by product name”.
This helps Tableau Agent understand both your intent (to create a calculation) as well as what you mean by the fields you want to calculate.
Calculation Descriptions
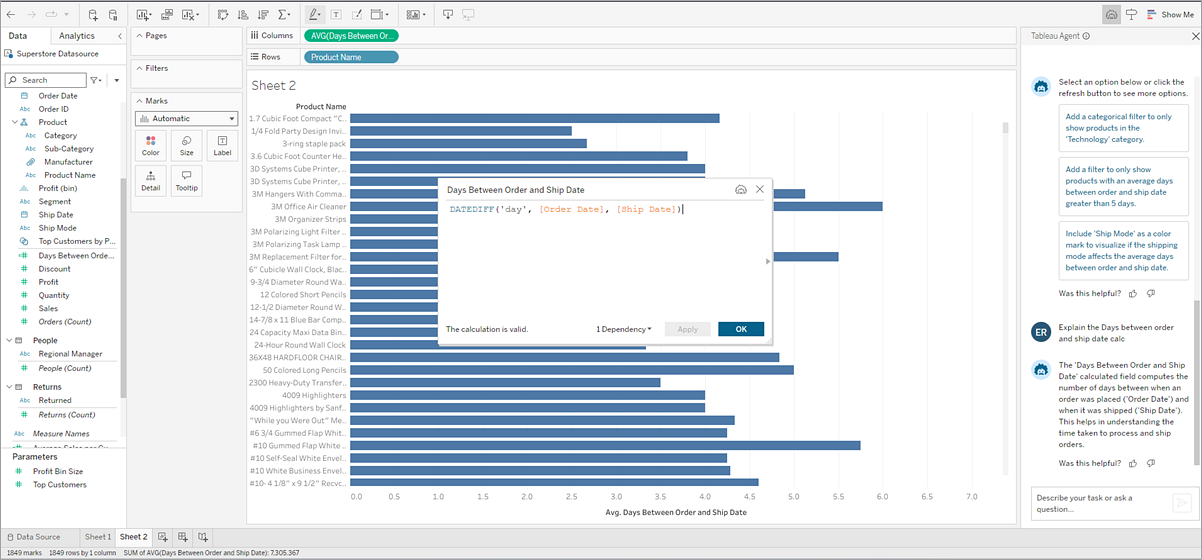
Understanding what a calculation does is just as important as creating the calculation itself. Tableau Agent can help with that.
Whether it’s a calculation that Tableau Agent created for you or one that exists as part of your data set, you can ask Tableau Agent to explain the calculation. For example, “Explain the Working Days Between Order and Ship calculation.”
Not only can this help you verify that the calculation does what you need, this feature can also help you build proficiency in using calculated fields in your Tableau analysis.
Edit calculations
You can edit any calculation that Tableau Agent created for you at any time. You can manually edit the calculation, or you can ask Tableau Agent to help you.
To edit a calculation, do the following:
In the conversation pane, find the calculation you want to edit.
Click Edit.
Manually make your changes in the Calculation Editor and click OK or describe the changes you want to make in the Tableau Agent conversation pane and let Tableau Agent make the changes for you.
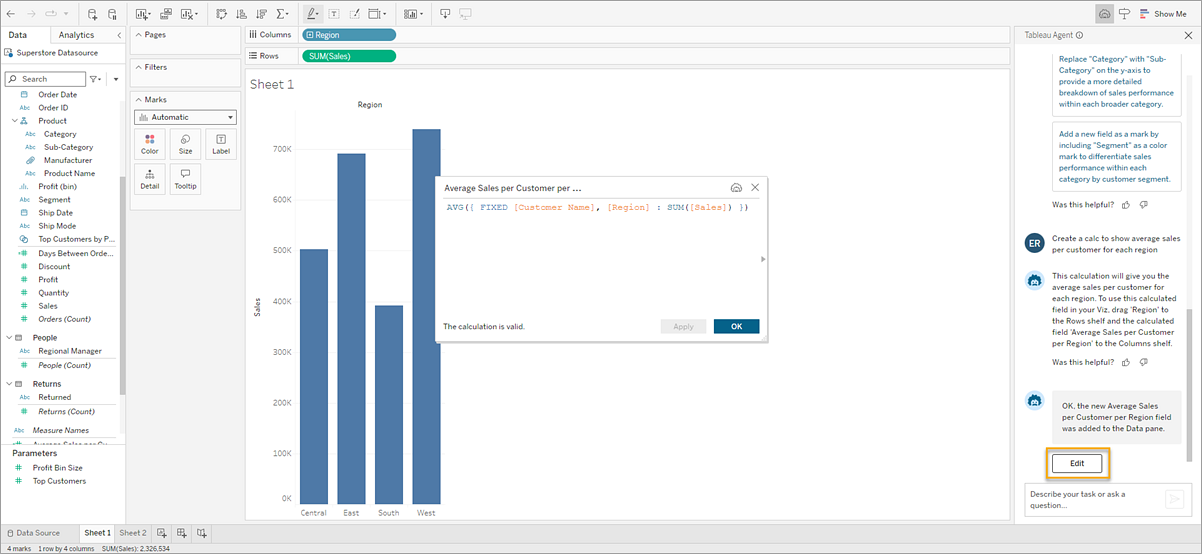
To ask Tableau Agent to update an existing calculation in the Data pane, open the calculation in the Calculation Editor first.
Right-click or Cmd+Click (MacOS) on the field in the Data pane.
Select Edit…
Manually make your changes in the Calculation Editor and click OK or describe the changes you want to make in the Tableau Agent conversation pane and let Tableau Agent make the changes for you.
Calculation limitations
When creating calculations using Tableau Agent, the following functionality is not yet supported:
When creating a calculation, Tableau Agent can't yet ask clarifying questions. You might need to be specific or iterate, such as specifying "change the field FIRST NAME into proper capitalisation" if there is more than one field with the word "name" in its name.
Available calculations can vary by connection type. For example, certain date functions such as DATEPARSE(Link opens in a new window) are only supported by data extracts and a subset of possible connectors.
If your request involves a function that isn't supported by your live data connection, Tableau Agent may create the calculation for you but it will be in an error state. To use the calculation, you'll need to take an extract of your data source first. In some cases, there may be alternative functions you can request, such as using DATE instead of DATEPARSE. For more information about these alternatives, see the functions documentation(Link opens in a new window).
Tableau Agent can’t create a calculation and then automatically use it in the viz. Instead, do this as a two-step process. Ask for the calculation and add it to the Data pane; then ask for the viz and reference the new calculated field by name.
Working with filters
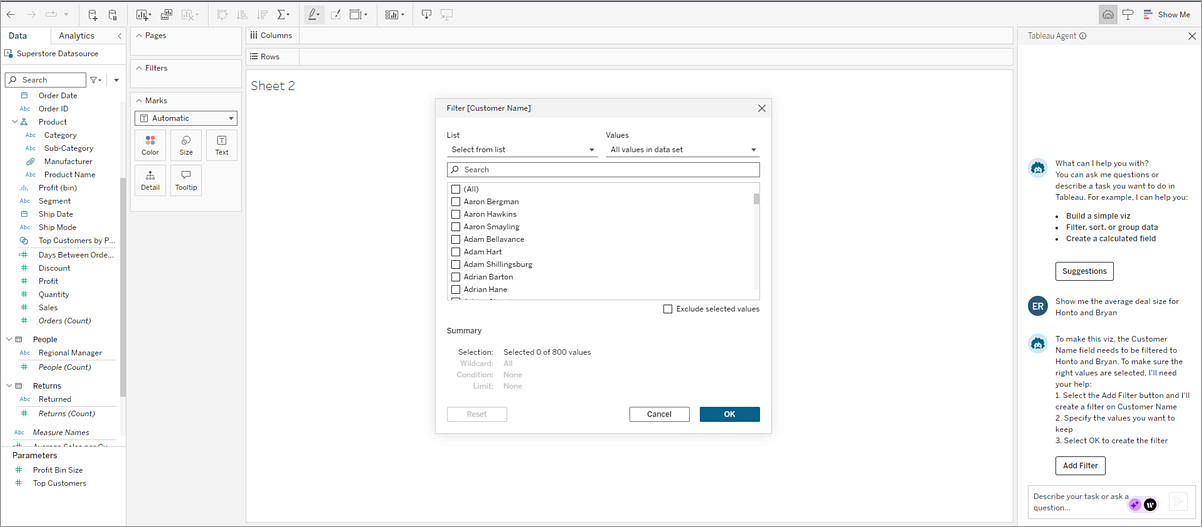
You can ask Tableau Agent to filter your viz using natural language. While Tableau Agent does its best to understand your request and return a solution, sometimes it might need your help to return the response that you're looking for. For example, if you have high-cardinality fields, fields with a lot of values, Tableau Agent might ask you to select the values you want.
In cases like this, you can select Add Filter in the Tableau Agent pane, and Tableau Agent opens the Filter dialog for you. Just select the values you want and select OK to add your filter to the viz.
Conversation history and viz recreation
You interact with Tableau Agent in the conversation pane. The pane is where Tableau Agent offers suggestions for analysis and maintains your conversation history for that session. If you ask a new question, the viz itself updates, but the conversation pane maintains a history of all your requests and Tableau Agent’s responses.
It also has interactive elements such as Retry with Tableau Agent  to ask Tableau Agent to query the LLM again with the same request and create another version of the viz, or Recreate
to ask Tableau Agent to query the LLM again with the same request and create another version of the viz, or Recreate  to go back to return to a previous viz without querying the LLM, maintaining the same results.
to go back to return to a previous viz without querying the LLM, maintaining the same results.
If you close and reopen the conversation pane while still in your same session, your conversation history persists. If you close your workbook, this clears the conversation with Tableau Agent. The conversation history isn’t saved and doesn’t appear the next time you open the published or saved workbook.
Tableau Agent is a per-sheet experience. There’s no awareness of other worksheets in your workbook and conversations can’t be shared between worksheets. If you change to a new sheet, this starts a new conversation.
If you want Tableau Agent to forget the context of what you’ve done so far, start a new sheet so there’s no history in the conversation pane.
Tips for getting the best results from Tableau Agent
Tableau Agent does its best to understand your intent and your data. But it’s still learning. Use the following tips to help Tableau Agent do its best and deliver great results for you.
| Tip | Problem | What to Do |
|---|---|---|
| Use clean data | Messy data is hard to analyse, and Tableau Agent won’t know how to clean and prep your data for you. |
|
| Hide irrelevant fields | Similarly named fields in your data set can be confusing to Tableau Agent. | Hide fields you don’t need and Tableau Agent won’t use these hidden fields. |
| Be careful with synonyms | Tableau Agent does a good job of understanding common synonyms. For example, it would know that “titles” and “films” could apply to a field called “movies”. However, it doesn’t know about any of your company-specific terminology or acronyms that you may use. | Refer to the specific fields you’re interested in to help Tableau Agent be more accurate. |
| Be explicit with your intent | Tableau Agent does its best to infer your intent, but it might not always get it right. | If you know you want Tableau Agent to generate a viz, use clues in your request like “show me”, “create a viz” or “build a bar chart”. Alternatively, if you want Tableau Agent to create a calculation, try starting your request with the phrase “Create a calc that...” |
| Specify how to evaluate “top” | Requests like “top products”, “best salespeople” and “highest quarter” can be ambiguous to Tableau Agent, and it might not know how to evaluate what “top”, “best” or “highest” is. | State how “top” should be measured and displayed. For example, try asking Tableau Agent to show you the “top 10 products based on profit” or “top 3 products based on sales volume”. |
| Use specific terminology in your requests | Tableau Agent can scan your data source for the field names and data in those fields, but it doesn't truly understand the data the way a human can. | The more descriptive you are in your request, the better Tableau Agent is at providing a relevant visualisation. If you know your data should be evaluated with an aggregation of MEDIAN instead of AVERAGE, specify that. |
| Break down complex tasks | Tableau Agent can’t update the data model and generate a visualisation as part of a single step. | Break down your tasks into parts and iterate. For example:
|
| Only ask questions about your data | Tableau Agent isn’t a general-purpose chatbot. It can’t answer consulting questions like “how should I analyse my data?” or general questions like “which cat breed makes the best pet?” | Ask questions targeted at analysing your data and iterating and digging deeper into the viz results. |
Be the human in the loop
As with all AI, its important to review the results you get when using Tableau Agent. Tableau Agent will do its best to understand your data and your intent when asking questions, but it might not always get it right.
For example, Tableau Agent tries to pick a default for things like date granularity (such as year, month or day) or aggregation (such as median or average). If you know the aggregation you want, it's better to specify this in your request.
If Tableau Agent gets it wrong, you can either restate your request and clarify what you want, or you can interact directly with the viz. After all, you're in the standard authoring environment and have access to all of Tableau's functionality.
You can also provide feedback at any time on the results with the “thumbs up” or “thumbs down” buttons, which show up with every Tableau Agent response.
If you click the “thumbs down” option, provide additional feedback to help improve Tableau Agent’s responses.
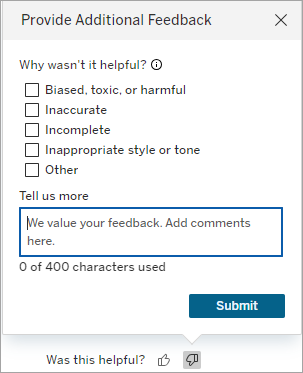
Tableau Agent limitations
Tableau provides powerful tools for the human analyst, and Tableau Agent is no different. AI in Tableau isn't meant to replace analysts and data explorers; it's here to give you a boost. Your participation in the process is crucial.
Types of analysis
Tableau Agent can't yet manage consultative questions like "How should I analyse my data?" or "Is there seasonality in this data?" Instead, you need to specify what you'd like to see, such as "What are my sales over time?"
Unsupported features
Tableau Agent doesn't have access to all of Tableau's authoring features – yet. It is currently available in web authoring and Tableau Desktop (starting in version 2025.1) if you are connected to a Tableau Cloud site with Tableau+ and AI in Tableau turned on in site settings, or if you are connected to a Tableau Server site (version 2025.3 and later) with AI in Tableau turned on.
Some things that Tableau Agent is currently unable to do include:
Choose a data source for you or do data modelling (such as creating joins or relationships)
Change data types, field roles or caption names
Format a viz, such as adding fields to the Marks card properties. For example, detail or tooltips.
Add reference lines
Organise or customise fields using groups, sets or parameters
Create interactivity with elements such as filter controls, parameters and actions
Build dashboards
Analyse large data sets. Tableau Agent will not work as well if you have hundreds or thousands of fields in your data set, especially if they are similarly named. If you try to filter against fields that are high cardinality (many distinct values for a single field), Tableau Agent might need you to manually perform your filter operations.
Block indexing refreshes after data model changes
Support all languages. Tableau Agent supports English (en_US) and a subset of other languages. If your data source field names and values are not in the same language as your user language settings or not the same as the language you are interacting with Agent in, use the exact field name and values in your requests. For information about the languages Tableau Agent currently supports, see AI in Tableau-supported languages and locales(Link opens in a new window).
