Let Site Users Request Access to Content
Permissions determine if a user has viewing access to a workbook, view, or other content inside a project. If a user clicks on content or a project they don’t have access to, they can send a request for access to the owner who controls permissions for that content.

When someone requests access, the owner who controls permissions for that content (either at the project or workbook level) receives an email with the name and email of the requester, the content or project requested, and a link to grant access to the content. In Tableau Server version 2022.3 and earlier, the owner receives a link to the content to manage permissions instead of a link to directly grant access.
-
On the email notification, select Grant Access.
-
On the dialog that appears, to grant the view permissions template, select Grant Access. To grant permissions other than the view template, select Manage Permissions.

If a user requests access to a workbook and content permissions are locked to the project, then the project owner receives the request. Likewise, if a user requests access to a workbook and project permissions are managed by the workbook owner, then the workbook owner receives the request.
After permission is granted, the owner can email the requester to let them know they have view capability to the project or workbook.
Default settings
The Request Access setting is enabled by default on a new site. To enable the setting if it's been disabled:
- Go to the General tab of the Settings page for your site.
- On the General tab, scroll down to Request Access and select Let users request access to projects, workbooks, and views.
- Click Save.
Configure project permissions
You can control who receives the access request by adjusting the project’s content permissions. If content permissions are:
- Locked to the project: the project owner receives the request.
- Managed by the owner: The workbook owner receives the request.
To manage content access using projects, see Use Projects to Manage Content Access and Permissions.
For more information about how permission rules are evaluated, see Permissions: Evaluate permission rules.
Change project permissions
For administrators and project leaders
Permissions can be set at the project level for both the project itself and for any content in the project. For example, if workbook permissions are configured at the project level, all workbooks published into that project inherit those default permissions. However, the can choose to change the permissions during publishing, or certain users can change the permissions on published content. To enforce the permissions established at the project level, Content Permissions can be locked to the project. For more information, see Lock asset permissions.
To set permissions at the project level:
- Navigate to the project
- Open the Actions menu (...) and click Permissions. The permissions dialog box opens.
- To modify an existing permission rule, select the rule and click the capability boxes to toggle through allowed/denied/unspecified.
- To create a new rule,
- Select + Add Group/User Rule.
- Select a group or user from the drop-down box. This creates a row where you can configure the permission rule.
- In the row for the permission rule
- choose an existing permission role template from the drop-down box for each content type tab.
- Or create a custom rule by navigating to a content type tab and clicking the capabilities. One click sets the capability to Allowed, two clicks sets it to Denied, and a third click clears the selection (Unspecified).

- When finished, click Save.
This dialog box has two main areas: permission rules at the top and the effective permissions grid below. Use the tabs to navigate between types of content.
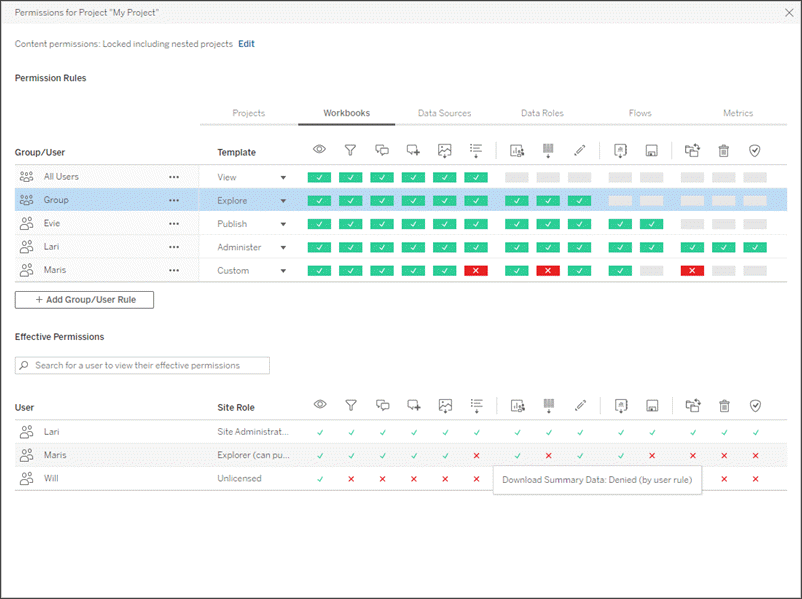
With a row selected at the top, the effective permissions grid populates. Use this to verify permissions. Hovering over a capability indicator provides information about why the capability is allowed or denied for that specific user.
Change content permissions
For administrators, project leaders, and content owners
If project permissions are not locked, permissions for individual pieces of content can be modified.
Warning: Tableau recommends managing permissions at the project level within the Tableau site. These steps are relevant only for content in projects where permissions are managed by the owner.
Set permissions on content
- Navigate to the content (workbook, data source, flow, data role)
- Open the Actions menu (...) and click Permissions. The permissions dialog box opens.
- To modify an existing permission rule, open the Actions menu (...) for that row and click Edit.
- To create a new rule,
- Select + Add a user or group rule.
- If necessary, use the drop-down box on the right to change between groups and users.
- Select a group or user from the drop-down box. This creates a row where you can configure the permission rule.
- In the row for the permission rule, choose an existing permissions role template from the drop-down box or create a custom rule by clicking the capabilities.
- When finished, click Save.
This dialog box has two main areas: permission rules at the top and the effective permissions grid below.

With a row selected at the top, the effective permissions grid populates. Use this to verify permissions. Hovering over a capability square provides information about why the capability is allowed or denied for that specific user.
One click sets the capability to Allowed, two clicks sets it to Denied, and a third click clears the selection (Unspecified).
Set permissions on a view
In some situations, it may be valuable to specify permissions on a view independently from the workbook that contains it. To set permissions on a published view, navigate to the view within a published workbook and follow steps above.
Warning: While it is possible to set view-level permissions within a workbook, we strongly recommend managing permissions at the project (or workbook) level as much as possible. For views to inherit permissions, the project must be locked or the workbook must be published with Show Sheets as Tabs. See Let Site Users Request Access to Content for more information.
