Skills by Tableau education role
This content is part of Tableau Blueprint – a maturity framework allowing you to zoom in and improve how your organisation uses data to drive impact. To begin your journey, take our assessment(Link opens in a new window).
The first step in educating your users is to understand the skills they will need in order to be successful in their roles. Successful data-driven organisations are supported by a wide variety of people, and needed skills range from successfully viewing and interacting with data to building high-availability into Tableau Server deployments.
The Executive advocacy and project team topic classifies users based on roles they will play in building your organisation's analytics strategy. Classifying users based on needed skills goes one step deeper. As you dig in, you will notice similarities among these roles, explained below.
Employees need to learn the Tableau skills unique to their roles and responsibilities within an organisation. We have categorised each unique set of Tableau skills as an education role. Education roles focus on the analytical and Tableau skills that users need to fulfil their day-to-day job responsibilities. In contrast, Tableau project team roles and responsibilities identify the deployment-related tasks and responsibilities for each project team member. Like project roles, education roles may not exactly match users’ organisational titles, but you can easily identify them by understanding the responsibilities of each role.
We identified twelve Education Roles that map to prescriptive Learning Paths that will educate employees in the skills needed to contribute to the growth of a data-driven organisation. We recommend that you review the education needs of different organisational roles even if you decide to self-curate education resources or to consume training courses individually.
Use the Education role mapping tab in the Tableau Blueprint Planner to begin building an education strategy by mapping job titles within your organisation to education roles.
Enable a data culture in your organisation
These roles establish cultural and technical standards to align every Tableau user to the analytics goals of your organisation.
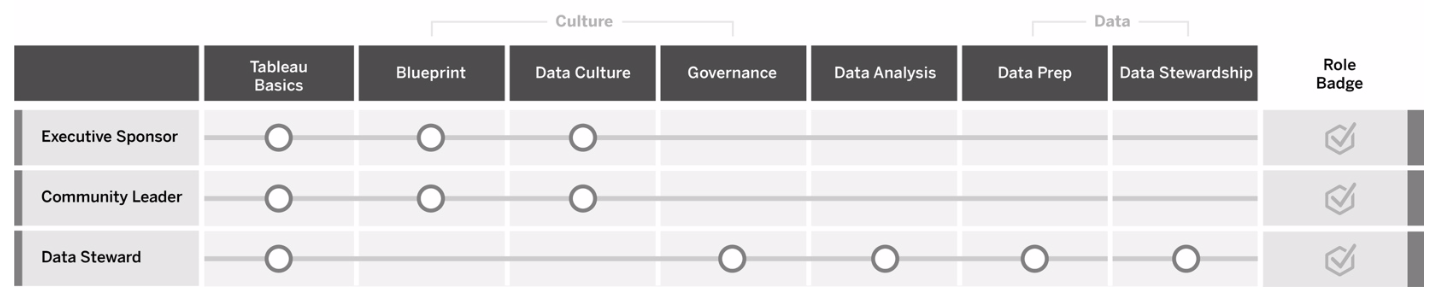
Executive Sponsor
Executive sponsors are responsible for driving the decisions and strategies that enable their organisation's continued growth and success. They understand market pressures, what it takes to stay competitive and how to lead their organisation forwards. These leaders recognise, embrace and promote the importance of implementing a data-driven culture to gain competitive advantage and understand the power of Tableau to achieve that goal. Licence types vary for executive sponsors based on where they are most active in their business. Their responsibilities include:
- Communicate and sell the vision for modern analytics across the organisation. Represent the interests of their respective departments to establish budget and funding.
- Align the use of analytics with strategic initiatives that drive organisational transformation.
- Approve Tableau governance processes, policies, guidelines, roles and responsibilities for managing their organisation's data in compliance with business and/or regulatory requirements identified by the project team.
- Set the example of using facts over intuition by placing data at the centre of every conversation in department meetings as a visible and vocal user of the platform.
Community Leader
Community leaders are responsible for coordinating efforts related to user enablement around communications, engagement and support. Most community leaders also fall into a role with heavy product usage, and will require a Creator subscription to understand how others are using Tableau. Their responsibilities include:
- Facilitate user-to-user connections within the organisation
- Coordinate engagement events for users within the organisation
- Promote support resources for users within the organisation
- Evangelise the use of analytics
Data Steward
Data Stewards understand the business domain and the interaction of business processes with analytics. Data stewards ensure there are documented procedures and guidelines for data access and use and work with database administrators and/or data engineers to plan and execute an enterprise-wide data governance, control and compliance policy. Within Tableau, they work to curate and manage certified data sources with set user permissions in accordance with enterprise governance policies. Data stewards are likely have a Creator licence and their responsibilities include:
- Ensure the accuracy, completeness, privacy and security of operational data.
- Ensure that the right data is available to the right people in the organisation.
- Understand the types of data the business needs.
Provide insights and develop visualisation solutions
These roles use the capabilities of the Tableau platform to consume & create business solutions that range from ad-hoc visualisations to embedded analytics.
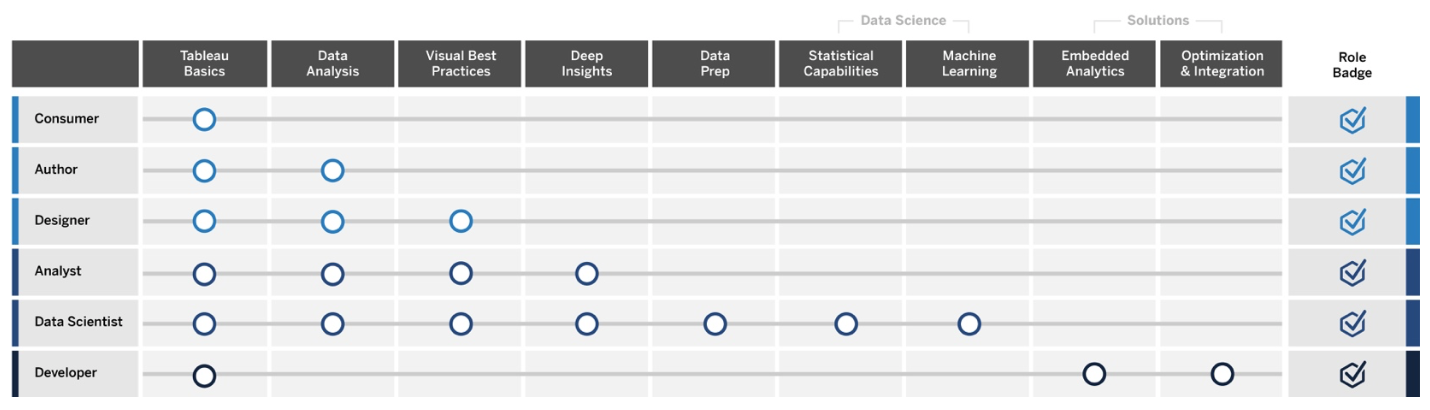
Consumer
Consumers use data to make more informed decisions for their lines of business. They can range from administrative assistants to C-suite executives, but they share a goal of making better, more informed business decisions based on dashboards and reports others in their organisation produce. Consumers likely have a Viewer licence and their responsibilities include:
- View reports and dashboards created by others and potentially serve as primary stakeholders of these dashboards.
- Use data to make decisions day-to-day job functions, keep informed of progress towards goals, and track team or company metrics.
- Stay knowledgeable in their subject areas even if they are not expert data analysts.
Author
Authors have a strong understanding of their market and business objectives, and they recognise the importance of making data-driven decisions. They leverage their foundational Tableau skills to make smarter business decisions more quickly by digging into their available data sources to create visualisations and dashboards mostly for their own consumption. Authors likely have a Creator licence, but may also author on the web with an Explorer licence. Their responsibilities include:
- Create and use existing data sources and create views and dashboards to provide actionable insights in Tableau Desktop.
- Perform basic analysis for personal use rather than for consumption by others, to increase personal job performance.
- Demonstrate knowledge of the area being analysed.
Designer
Designers create visualisations and dashboards that help stakeholders across their organisation absorb information quickly and easily. They use Tableau to deliver beautiful, functional, and impactful dashboards. They draw on their appreciation of the art of visual design as a clear communication tool and on their understanding of the impact that clear and engaging visualisations can have on both internal and external audiences. Designers likely have a Creator licence and their responsibilities include:
- Demonstrate passion about visualisation layout, colour, appearance and functionality.
- Ensure that their visualisations convey information accurately and efficiently to their audience.
- Create appealing dashboards that make it easy for users to explore data and gain insights.
Analyst
Analysts are responsible for supporting their lines of business to deliver valuable insights from data. Analysts work with complex data sources, use advanced calculations to customise data, and use advanced features (parameters, sets, filters and forecasting) to build a range of charts and to analyse a variety of data types. Analysts perform ad-hoc analysis to help explore new data questions, produce well-designed interactive dashboards that present data accurately, and create and share data insights within their organisations for the purpose of guiding business decisions and outcomes. Analysts likely have a Creator licence and their responsibilities include:
- Create reports and dashboards for others in the organisation to consume or iterate on.
- Perform ad-hoc exploration of data to highlight business opportunities.
- Conduct meaningful data analysis to inform business decisions.
Data Scientist
Data scientists are experts at deriving valuable insights for large and varied data sets. They are adept at tackling big data, know how to apply advanced analytic capabilities to answer business questions, are often domain experts, and work collaboratively across the business and IT to deliver ROI from data. They can reduce data cleansing and preparation time in Tableau Prep Builder, use Tableau Desktop for exploratory analysis, and develop final dashboards to support and clearly present project findings. Data scientists likely have a Creator licence and their responsibilities include:
- Build and deploy end-to-end solutions leveraging machine learning and advanced analytics.
- Build and test models in R, Python, or other coding languages, perform simulations and tune models for enterprise production.
- Work with stakeholders throughout the organisation to identify opportunities for leveraging company data to drive business solutions.
Developer
Developers translate the needs of the business into the software tools, applications and automated processes that keep their organisations lean, smart and efficient. They leverage Tableau to create new data products, embed visualisations and dashboards into current solutions, improve analytical processes and integrate organisational insights into other external platforms and portals. Developers are likely have a Creator licence and their responsibilities include:
- Embed and integrate Tableau vizzes into internal and external web applications (e.g. Salesforce).
- Script automation tasks.
- Build web data connections to bring in data from sources without native connectors in Tableau.
- Create custom data extracts.
- Create dashboard extension add-ins for customised workflows in Tableau.
Deploy and manage Tableau
These roles plan scalable deployments of Tableau Server or Tableau Cloud, and once in production ensure that users can access what they need when they need it.
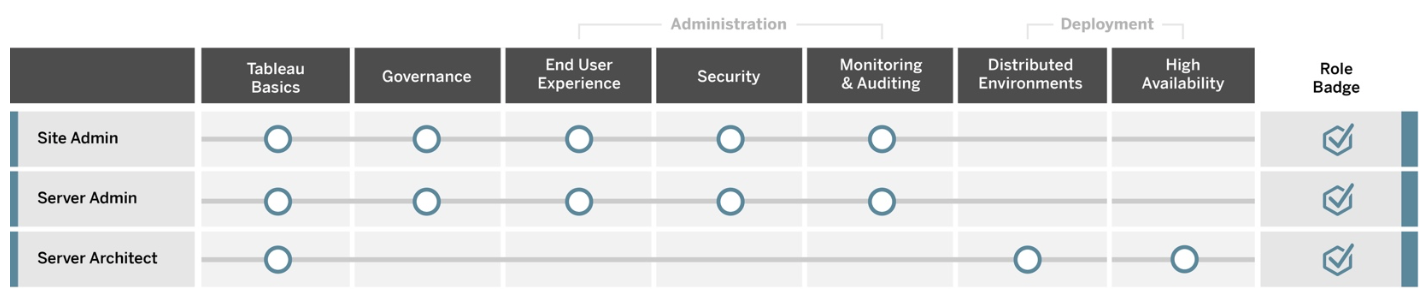
Site Administrator
Site administrators manage, monitor and maintain sites on Tableau Server or Tableau Cloud. They manage site organisation, content publishing, groups, users and permissions. Through their monitoring efforts, they know the latest details on site utilisation, adoption, performance and compliance. Site administrators are key to the adoption of Tableau Server or Tableau Cloud in their organisations. Site administrators have a Creator licence and their responsibilities include:
- Create and manage site users and groups.
- Create projects to organise site content.
- Assign content permissions to users and groups.
- Monitor site metrics such as content usage, success of extract refresh tasks and user activity.
- Troubleshoot user issues with a site.
Server Administrator
Server administrators ensure that their installation of Tableau Server runs smoothly. Key elements include securing the server, managing licences, managing users, monitoring and troubleshooting server issues, and performing server maintenance. Server administrators work tirelessly to ensure that Tableau Server is not only operational but meets the ongoing needs of the enterprise. Server administrators have a Creator licence and their responsibilities include:
- Install and configure Tableau Server.
- Perform server maintenance (e.g. backups, updates).
- Monitor server performance and usage.
- Manage all sites, users, groups and content on Tableau Server.
- Create sites.
Server Architect
Server architects plan Tableau Server deployments and ensure their success. Key success factors include integrating the deployment with preferred authentication options, monitoring the server and scaling server overtime to meet enterprise demand. Once implementation is complete, server architects maintain the deployment and help to investigate and resolve server issues. Their responsibilities include:
- Plan enterprise server deployments.
- Configure server authentication options.
- Monitor, maintain and scale server deployments to satisfy business requirements.
- Automate server monitoring and maintenance tasks.
- Investigate and resolve server issues.
