Self-Deploy Tableau Server on Microsoft Azure in a Distributed Environment
This is archived content
Deployments on public clouds continue to be supported but the content for third-party public cloud deployments is no longer updated.
For the latest Tableau Server deployment content, see the Deploy(Link opens in a new window) section of Tableau Server help.
For those customers who have access, we recommend Tableau Cloud. For more details, see:
- Tableau Cloud Manual Migration Guide
- Tableau Cloud Trial for Admin(Link opens in a new window)
- Tableau Cloud: Get Started for Admin(Link opens in a new window)
Introduction
You can run Tableau Server on two virtual machines (VMs) in a distributed environment, also known as a cluster. However, if you want to run Tableau Server in a highly available (HA) distributed environment, you need to launch three or more Microsoft Azure virtual machines (VMs) of the same type and capacity and configure them as worker nodes. This scenario assumes that you have three Microsoft Azure VMs with Tableau Server installed on each instance. One instance is configured as the primary node, and the other two instances are configured as additional nodes.
Use the following steps to install and deploy Tableau Server on a cluster of three Microsoft Azure VMs in a highly available and scalable configuration.
Step 1: Create an Azure Virtual Network (VNet)
You must have an existing Azure Virtual Network (VNet) with a private subnet spanning three Availability Zones. For information about how to plan and create a VNet with public and private subnets, see Azure Virtual Network(Link opens in a new window), Plan and design Azure Virtual Networks(Link opens in a new window), and Create a virtual network with multiple subnets (Link opens in a new window)at the Microsoft Azure website.
(Optional) Step 2: Create an Azure Active Directory Service for the VNet
Follow the steps in Enable Azure Active Directory Domain Services using the Azure portal(Link opens in a new window), at the Microsoft Azure website, to create a fully-managed Samba-based directory in Microsoft Azure. When you create a directory with Microsoft AD, the Azure Active Directory Service creates two directory servers and DNS servers. The directory servers are created in different subnets in your virtual network for redundancy, so that your directory remains accessible even if a failure occurs.
Use the private subnet within your Azure VNet to create the Microsoft AD so that you can run Tableau Server across Availability Zones.
Note: If you want to use SSL with your deployment, use Microsoft Azure Application Gateway instead of the Microsoft Azure Load Balancer.
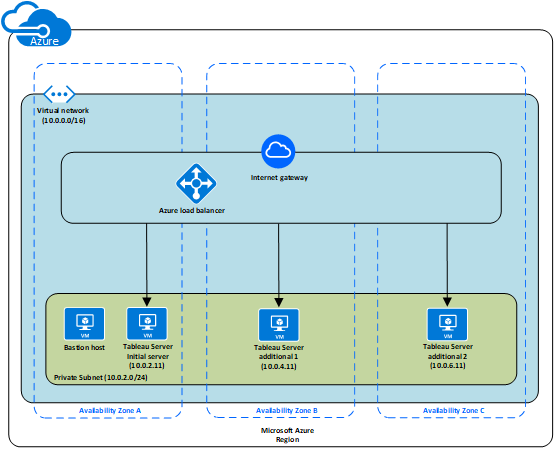
Step 3: Deploy Three Azure VMs
Deploy three Microsoft Azure virtual machines (VMs) across three Availability Zones. Be sure to select a region that supports Availability Zones. Select a VM that meets the system requirements for Tableau Server. You’ll use one node as the initial server and two new nodes as additional servers. All of the instances should be of the same type and capacity.
After you have launched the Microsoft Azure VMs, connect to them from one of the Remote Desktop Gateway (RDGW) instances by using the credentials that you decrypted for the local administrator account.
Step 4: Install and Configure Tableau Server
You’ll install Tableau Server on the Microsoft Azure virtual machines (VMs) you launched in Self-Deploy Tableau Server on Microsoft Azure in a Distributed Environment and configure the instances as an initial server and the rest as additional servers. For more information about installing and configuring Tableau Server on an initial server and on additional servers, see Install and Configure Additional Nodes.
Use a bastion host to manage access to VMs within the virtual network. For more information, see Planning a bastion environment(Link opens in a new window) at the Microsoft Azure website.
Step 5: Create an Azure Load Balancer for the Tableau Server Cluster
Read the Azure Load Balancer overview(Link opens in a new window) at the Microsoft Azure website and follow the steps to launch a load balancer within your Azure Virtual Network (VNet).
-
Create and launch either an Internet-facing load balancer or an internally accessible load balancer:
-
To launch a public, Internet-facing load balancer, follow the steps in Load balance VMs across availability zones with a Standard Load Balancer using the Azure portal(Link opens in a new window) at the Microsoft Azure website, and select the two public subnets. Make sure that you configure the load balancer with SSL, as explained in Configure an application gateway for SSL offload by using the Azure portal(Link opens in a new window) at the Microsoft Azure website.
-
To launch an internally accessible load balancer, follow the steps in Create an Internal load balancer in the Azure portal(Link opens in a new window) at the Microsoft Azure website, and select the two private subnets.
-
-
Ensure that your security group is configured to allow access on port 80 or 443 only, with the source limited to hosts or ranges of hosts that will access Tableau Server.
-
Specify the ping path as /.
-
Select the Tableau Server instances and ensure that Enable CrossZone Load Balancing is selected so that the load balancer can load-balance the traffic across the instances in multiple Availability Zones.
-
Update Tableau Server to use the load balancer. For more information, see Add a Load Balancer in the Tableau Server Help.
