Set Up Amazon Redshift IAM Identity Centre OAuth
These instructions are for the newer AWS IAM IDC service. For original IAM integration, see Set Up Amazon Redshift IAM OAuth.
Depending on the identity provider, there are different steps needed to configure the integration. This is a high-level overview. Tableau cannot provide detailed instructions for how to configure AWS or the IDP, but this is the general approach.
For some detailed examples of implementing authentication with Redshift, see "Integrate Tableau and Okta with Amazon Redshift using AWS IAM Identity Centre(Link opens in a new window)" and "Integrate Tableau and Microsoft Entra ID with Amazon Redshift using AWS IAM Identity Centre(Link opens in a new window)".
Note: Single-use refresh tokens (sometimes called rolling refresh tokens or refresh token rotation) are not supported for OAuth connections to Tableau at this time. Support for these tokens is planned for a future release.
Step 1: Configure the IDP
Create OAuth clients on the IDP for Tableau Desktop and Tableau Server or Tableau Cloud. The Desktop client should enable
PKCEand usehttp://localhostredirects.Add any required custom claims to use for authorisation to roles.
Create the Tableau OAuth config files. See documentation on GitHub(Link opens in a new window), and examples(Link opens in a new window). We welcome examples for other IDPs.
Be sure to prefix the Tableau OAuth config IDs with “
custom_”.Note: OAuth config IDs have a maximum limit of 36 characters. IDs longer than this may not generate an error, but they will not work.
If your IDP supports dynamic localhost port then disable
OAUTH_CAP_FIXED_PORT_IN_CALLBACK_URL. If it does not, make sure to add several localhost callback URLs to the allowlist in the config file and on the IDP.
Install the new Tableau OAuth configuration files in the
OAuthConfigsfolder associated with each application on desktop hosts (Tableau Desktop, Tableau Prep Builder, Tableau Bridge), and on each Tableau Server and Tableau Cloud site that will be using OAuth.
Step 2: Configure IDP and Roles on AWS
See your AWS documentation for information on doing this.
Step 3: Connect to Redshift
Connect to Redshift.
Select OAuth for Authentication.
Select Identity Centre for Federation Type.
(Optional) Specify the Identity Centre Namespace if necessary.
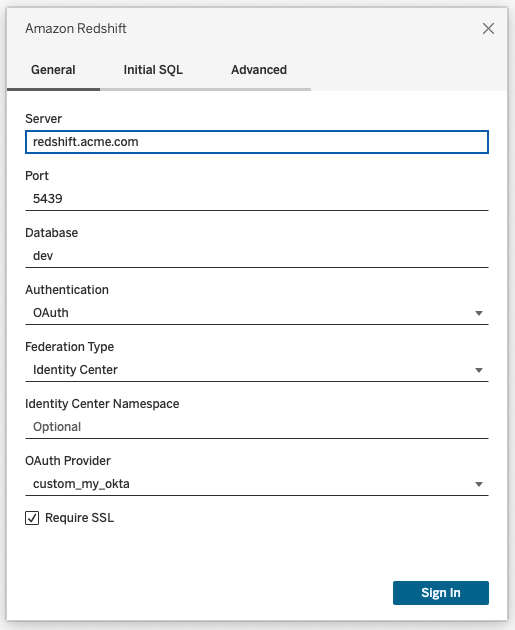
When correctly configured, you will be redirected to the IDP to authenticate and authorise tokens for Tableau. Tableau will receive an access token and refresh tokens. It will send the access token to the driver for authentication.
Tokens
By default, Redshift OAuth to IAM IDC passes the access token to the driver. For on-premise customers, including those using Tableau Bridge, you may use a TDC file to pass the ID token instead.
<connection-customization class='redshift' enabled='true' version='10.0'> <vendor name='redshift' /> <driver name='redshift' /> <customizations> <customization name='CAP_OAUTH_FEDERATE_ID_TOKEN' value='yes'/> </customizations> </connection-customization>
For more information about configuring and installing .tdc files, see Customise and Tune a Connection(Link opens in a new window) and Using a .tdc File with Tableau Server(Link opens in a new window).
Okta
If you are using Okta, it's better to use a "custom authorisation server" instead of the "org authorisation server". The custom authorisation servers are more flexible. A custom authorisation server is created by default and called "default". The authorisation URL should look like this:
https://${yourOktaDomain}/oauth2/{authServerName}/v1/authorize
Update the driver
For Redshift OAuth using the IAM IDC service, you need to use at least version 2.x of the ODBC driver. Download the latest version of the Redshift ODBC driver found on https://github.com/aws/amazon-redshift-odbc-driver/tags(Link opens in a new window). Note that there is no v2 driver yet for OSX.
Troubleshooting Redshift IAM IDC OAuth
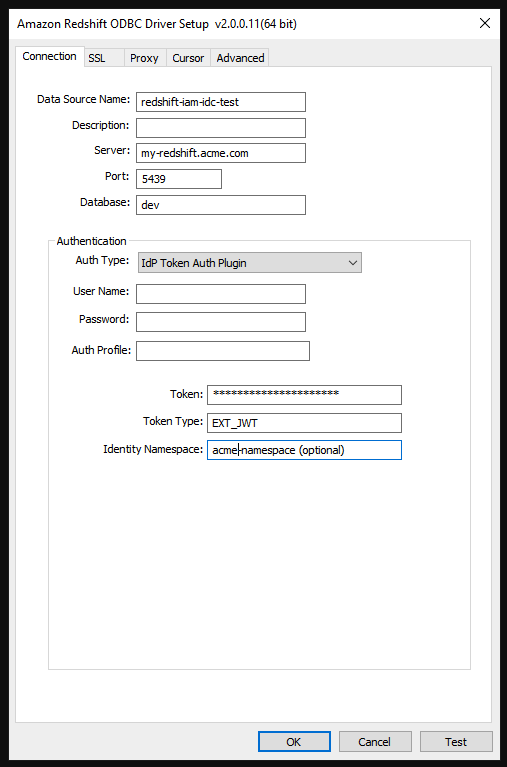
The best way to diagnose errors is to remove Tableau from the picture. You can instead test using the driver manager or a similar tool. This is just for troubleshooting – you shouldn't use a DSN or the "Other ODBC" connector for regular usage of this feature. To help ensure a valid test, the parameters should be the same as shown below, except for the cluster information, database, token and namespace.
If you see an error message about invalid/expired token coming from the driver on the first connection (it will have a SQLState error code like [28000] or [08001] in the error message), then Tableau successfully completed the OAuth flow, and failed in the driver. This means there is a misconfiguration on either the AWS side or the IDP side. There may also be permissions or authorisation errors returned from the driver, which is also out of Tableau's control.
Before you begin testing, you first need to get an access token (the default for IAM IDC) or refresh token (if customised) to send to the driver.
Here is an example with Okta. Almost all IDPs have a way to do this which is quite similar. Note that to use this flow you need to have enabled resource owner password grant type. Substitute the IDP URL, client secret, client ID, username and password.
curl -X POST "https://OKTA_URL/v1/token" \
-H 'accept: application/json' \
-H "Authorization: Basic $(echo -n 'CLIENTID:CLIENTSECRET' | base64)" \
-H "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded" \
-d "grant_type=password&username=USER&password=PASSWORD&scope=openid"
Once you have the token, you can use a DSN to test. For Windows, you can use the ODBC driver manager. On Linux you can use the isql command line tool that is included with Tableau Server in the customer-bin folder.
Tableau recommends you do not use other plugins to test, because they may not work in a server environment. They either use a fixed AWS profile or require direct access to a browser.
Below is an example of using the ODBC driver manager on Windows.